Buzz Haven: Your Source for Trending Insights
Stay updated with the latest buzz in news, trends, and lifestyle.
Web Accessibility: Not Just for the Bold and Beautiful
Unlock the secrets of web accessibility! Discover why it's essential for every user, not just the bold and beautiful. Transform your site today!
What is Web Accessibility and Why Does It Matter?
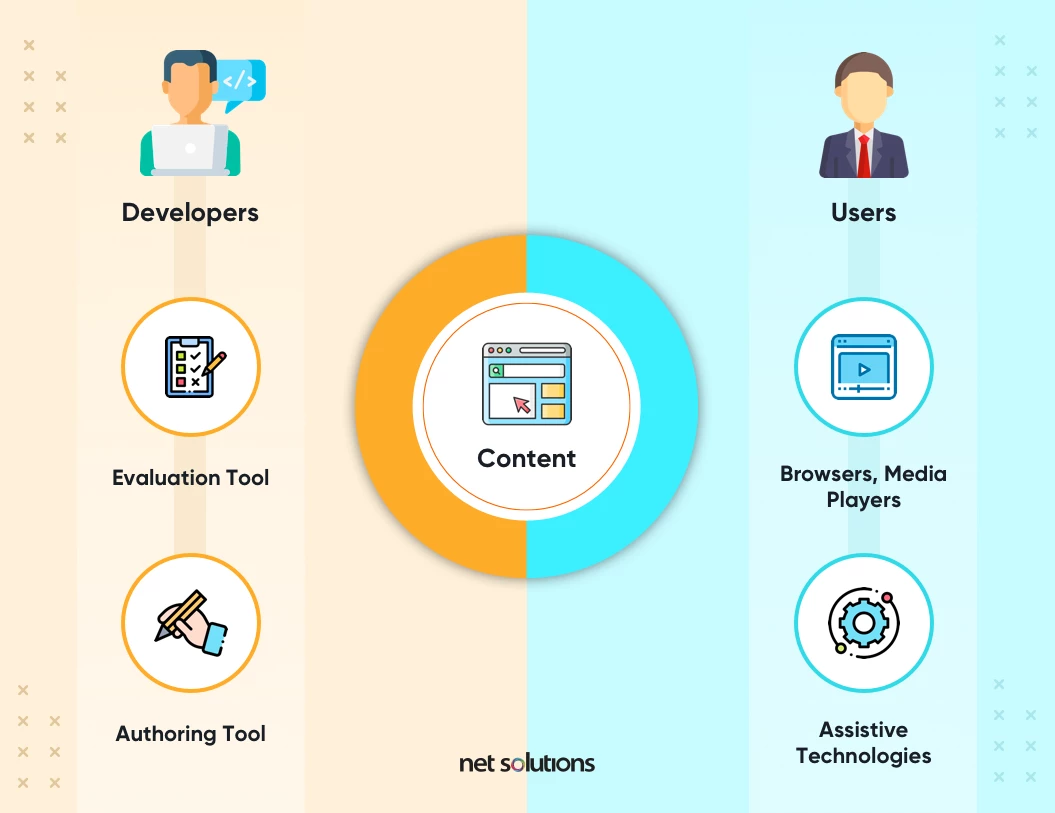
Web accessibility refers to the practice of ensuring that websites, tools, and technologies are designed and developed so that people with disabilities can use them effectively. This includes individuals with visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive impairments. By adhering to web accessibility standards, such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), developers can create more inclusive digital environments that allow everyone to access the information and services they need. When websites are accessible, it not only enhances usability for those with disabilities but also improves the overall user experience for all visitors.
Beyond ethical considerations, web accessibility is vital for expanding reach and enhancing engagement. A website that is designed with accessibility in mind can attract a wider audience, as approximately 15% of the global population lives with some form of disability. Additionally, making your site accessible can improve your SEO performance, as search engines favor websites that provide high-quality user experiences. In today’s digital landscape, prioritizing web accessibility is not just a regulatory requirement; it is a fundamental component of an inclusive strategy that demonstrates respect for all users.
Top 10 Web Accessibility Best Practices You Should Know
Web accessibility is crucial for ensuring that all users, including those with disabilities, can navigate and interact with your website effectively. Here are the top 10 web accessibility best practices you should know:
- Use semantic HTML elements to improve the understanding of your content by assistive technologies.
- Ensure that text has sufficient contrast against its background to enhance readability.
- Provide alternative text for images to describe visual content to users who rely on screen readers.
- Implement keyboard navigability, allowing users to access all interactive elements without a mouse.
- Utilize ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) roles and properties to supplement HTML where necessary.
Continuing with these web accessibility best practices, you should also consider the following:
- Make sure forms are accessible by labeling elements clearly and providing descriptive error messages.
- Avoid autoplay media, giving users the ability to control their experience.
- Ensure your website is responsive and works well on various devices, including mobile phones and tablets.
- Regularly test your website using accessibility evaluation tools to identify and rectify issues.
- Stay updated on the latest accessibility guidelines and standards, such as WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines), to enhance your practices.
How to Make Your Website Inclusive for Everyone: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating an inclusive website is crucial for ensuring that all users, regardless of their abilities or backgrounds, can access your content. To start, it's important to consider web accessibility guidelines. Begin by implementing semantic HTML to provide context and structure for assistive technologies. Use headings (<h1>, <h2>, etc.) effectively to lay out your content hierarchically. Ensure that all images have alt text descriptions, which help visually impaired users understand image content. Finally, test your website's color contrast to accommodate users with visual impairments, adhering to the WCAG standards.
Next, consider providing multiple means of engagement and interaction on your site. This can include offering transcriptions for audio and video content, and ensuring that all interactive elements, like forms and buttons, are keyboard-navigable. Utilize clear language for your written content, avoiding jargon where possible, and ensuring that instructions are straightforward. Lastly, conduct user testing with individuals from diverse backgrounds to gather feedback, making iterative changes based on their experiences and suggestions. By embracing these practices, you not only make your website inclusive but also broaden your audience reach.