Buzz Haven: Your Source for Trending Insights
Stay updated with the latest buzz in news, trends, and lifestyle.
When Your Dinner Turns into a Nightmare: Tales of Food Poisoning
Discover chilling stories of food poisoning nightmares that will make you think twice before your next meal!
Common Symptoms of Food Poisoning: When to Seek Help
Food poisoning can occur after consuming contaminated food or beverages, leading to a variety of symptoms that can range from mild to severe. Common symptoms of food poisoning include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever. While many individuals may experience a combination of these symptoms, it is important to recognize the severity of your condition. If symptoms persist for more than 24 hours, or if you develop a high fever (over 101.5°F), it's crucial to seek medical attention to prevent further complications.
In addition to the typical symptoms, individuals may also experience dehydration due to loss of fluids from vomiting and diarrhea. Signs of dehydration include extreme thirst, dark urine, dizziness, and dry mouth. If you notice these symptoms alongside gastrointestinal distress, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider. When to seek help can depend on the severity and duration of your symptoms; if you are unable to keep fluids down or if you have blood in your stool, do not hesitate to visit a medical professional for assessment and treatment.
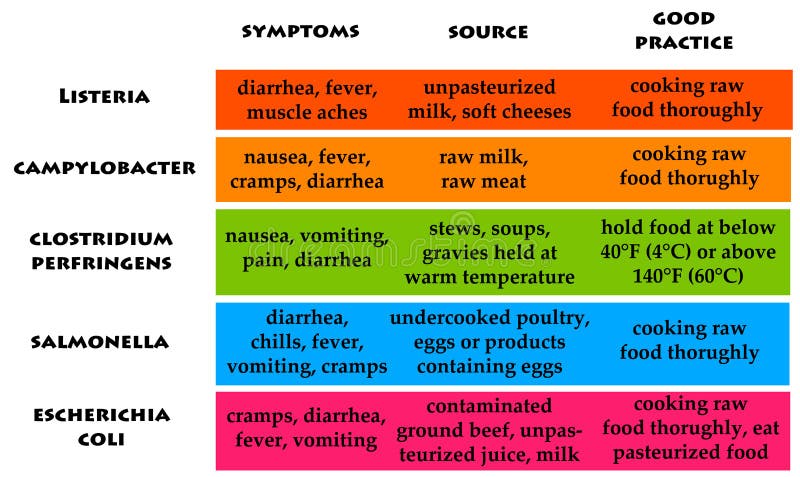
The Most Frequent Causes of Foodborne Illness: Are You at Risk?
Foodborne illness, commonly referred to as food poisoning, is an unfortunate yet prevalent issue that can affect anyone. Common causes of foodborne illnesses include improper food handling, undercooked food, and cross-contamination. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the most frequent culprits are salmonella, norovirus, and E. coli. These pathogens can thrive in environments where proper food safety practices are not followed, putting you at risk every time you consume food that may be contaminated.
Understanding these risks is essential for preventing foodborne illnesses. Here are some tips to minimize your risk:
- Wash your hands before and after handling food.
- Keep raw meats separate from other foods to avoid cross-contamination.
- Cook foods to their appropriate temperatures to ensure pathogens are destroyed.
- Refrigerate leftovers promptly to prevent bacterial growth.
By following these guidelines, you can significantly reduce your chances of experiencing the unpleasant effects of foodborne illness.
How to Prevent Food Poisoning at Home: Tips for Safe Cooking
Preventing food poisoning at home begins with proper food handling techniques. Start by ensuring that your kitchen is clean and organized. Always wash your hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds before and after handling food, especially raw meat, poultry, and seafood. Additionally, avoid cross-contamination by using separate cutting boards for raw and cooked foods. Use a food thermometer to ensure that all meats are cooked to their safe minimum internal temperatures: 165°F for poultry, 160°F for ground meats, and 145°F for whole cuts of meat.
Another crucial tip for safe cooking is to store food properly. Keep your refrigerator at or below 40°F and your freezer at 0°F to inhibit bacterial growth. Leftovers should be stored in airtight containers and consumed within three to four days. Always remember to check expiration dates and discard any food products that appear spoiled or have developed an off smell. Following these guidelines will significantly reduce your risk of food poisoning and help you maintain a safe cooking environment.